JavaScript Guides Advanced
9 JavaScript Tips You May Not Know
JavaScript is a fully-featured Object-Oriented programming language, on the surface, it shares syntactical similarities
with Java and C, but the mentality is quite different, at its core, JavaScript is more similar to functional languages.
Inside is a list of JavaScript tips, some offer techniques to simulate features found in C-like languages (such as
assertions or static variables), others are meant to improve performance and explore some of the more obscure
parts of the web scripting language
1. Arrays as Multipurpose Data Structures
Although that JavaScript may seem limited on the data structure front at first glance, its Array class is much more
versatile than the usual array type found in other programming languages (like C++ or Java), it's commonly used as
an array or associative array, and this tip demonstrates how to use it as a stack, queue, and binary tree. Re-using
the Array class instead of writing such data structures provides two benefits: First, time isn't wasted rewriting
existing functionality, and second, the built-in browser implementation will be more efficient than its JavaScript
counterpart.
Stack
A stack follows the Last-In First-Out (LIFO) paradigm, an item added last will be removed first. The Array class
has 2 methods that provide stack functionality, they are push() and pop(), push() appends an item to the end of the
array, and pop() removes and returns the last item in the array, the next code block demonstrates how to utilize
each of them:
var stack = [];
stack.push(2); // stack is now [2]
stack.push(5); // stack is now [2, 5]
var i = stack.pop(); // stack is now [2]
alert(i); // displays 5
Queue
A queue follows the First-In First-Out (FIFO) paradigm, the first item added will be the first item removed, an
array can be turned into a queue by using the push() and shift() methods, push() inserts the passed argument at the
end of the array, and shift() removes and returns the first item, let's see how to use them:
var queue = [];
queue.push(2); // queue is now [2]
queue.push(5); // queue is now [2, 5]
var i = queue.shift(); // queue is now [5]
alert(i); // displays 2
It's worth noting that Array also has a function named unshift(), it adds the passed item to the beginning of an array,
so a stack can also be simulated by using unshift()/shift() and a queue can be simulated by using unshift()/pop().
If all these function names are confusing, you may create aliases with your own names, for example, to create a
queue with methods named add and remove:
var queue = [];
queue.add = queue.push;
queue.remove = queue.shift;
queue.add(1);
var i = queue.remove();
alert(i);
Binary Tree
A binary tree represents data in a tree of nodes, each node has a value and two children (left and right). In C, this
data structure is usually implemented using structures and pointers, this implementation is possible to do in
JavaScript using objects and references, however, for smaller trees, there is an easier and quicker way using only
one array, the first item of the array will be the head of the tree, indexes of left and right child nodes if node i can be
calculated using the following formula:
leftChild(i) = 2i + 1
rightChild(i) = 2i + 2
This image illustrates the method (courtesy of Wikipedia):
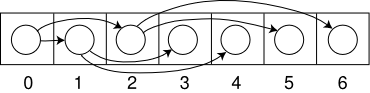
As you see, this method isn't exclusive to JavaScript, but it can be very useful when dealing with small trees, you
can for example write your own helper functions for getting and setting a node's value or children, and traversing the
tree, and those methods will be as simple as doing arithmetic calculations and/or for loops. On the other hand, the
disadvantage of this method is that wasted space grows as the depth of the tree increases.
2. String Concatenation vs. Array.join
This cannot be stressed enough, doing many string concatenation operations can be a major hit on performance,
and it's easy to avoid in many situations, consider for example that you want to build a string out of many pieces,
one bad way to do this is using the + to concatenate all pieces into a huge string, one piece at a time:
str = '';
for (/* each piece */) {
str += piece; // bad for performance!
}
return str;
This method will result in too many intermediate strings and concatenation operations, and will poorly perform
overall.
A better approach to this problem is using Array.join(), this method joins all array elements into one string:
var tmp = [];
for (/* each piece */) {
tmp.push(piece);
}
str = tmp.join(''); // Specified an empty separator, thanks Jonathan
return str;
This method doesn't suffer from the extra string objects, and generally executes faster.
3. Binding Methods To Objects
Anyone who works with JavaScript events may have come across a situation in which they need to assign an
object's method to an event handler, the problem here is that event handlers are called in the context of their HTML
element, even if they were originally bound to another object, to overcome this, I use a function that binds a method
to an object, it takes an object and method, and returns a function that always calls the method in the context of that
object, I found the trick in Prototype, and wrote the following function to use it in projects that don't include
Prototype:
function bind(obj, method) {
return function() { return method.apply(obj, arguments); }
} And this snippet shows how to use the function:
var obj = { msg: 'Name is', buildMessage: function (name) { return this.msg + ' ' + name; } } alert(obj.buildMessage('John')); // displays: Name is John f = obj.buildMessage; alert(f('Smith')); // displays: undefined Smith g = bind(obj, obj.buildMessage); alert(g('Smith')); // displays: Name is Smith
4. Sorting With a Custom Comparison Function
Sorting is a common task, JavaScript provides a method for sorting arrays, however, the method sorts in
alphabetical order by default, non-string elements are converted to strings before sorting, which leads to
unexpected results when working with numbers:
var list = [5, 10, 2, 1];
list.sort()
// list is now: [1, 10, 2, 5]
The explanation of this behavior is simple: Numbers are converted to strings before sorting them, so 10 becomes
'10' and 2 becomes '2', the JavaScript interpreter compares two strings by comparing the first two characters of
each, str1 is considered "less than" str2 if str1's first character comes before str2's first character in the character
set, in our case, '1' comes before '2' so '10' is less than '2'.
Fortunately, JavaScript provides a way to override this behavior by letting us supply a comparison function, this
function defines how elements are sorted, it takes two compared elements a and b as parameters, and should
return:
- A value less than zero if a < b.
- zero if a == b.
- A value greater than zero if a > b.
Programming such a function for number comparison is trivial:
function cmp(a, b) {
return a - b;
} Now we can sort our array using this function:
var list = [5, 10, 2, 1]; list.sort(cmp); // list is now: [1, 2, 5, 10]
This flexibility in Array.sort() allows for more sophisticated sorting, let's say you have an array of forum posts, each
post looks something like:
var post = {
id: 1,
author: '...',
title: '...',
body: '...'
}
If you want to sort the array by post id's, create the following comparison function:
function postCmp(a, b) {
return a.id - b.id;
}
It's reasonable to say that sorting using a native browser method is going to be more efficient than implementing a
sort function in JavaScript, of course, data should be sorted server-side if possible, so this shouldn't be used unless
absolutely necessary (for example, when you want to offer more than one sort order on one page, and do the
sorting in JavaScript).
5. Assertion
Assertion is one of the commonly-used debugging techniques, it's used to ensure that an expression evaluates to
true during execution, if the expression evaluates to false, this indicates a possible bug in code, JavaScript lacks a
built-in assert function, but fortunately it's easy to write one, the following implementation throws an exception of
type AssertException if the passed expression evaluates to false:
function AssertException(message) { this.message = message; }
AssertException.prototype.toString = function () {
return 'AssertException: ' + this.message;
}
function assert(exp, message) {
if (!exp) {
throw new AssertException(message);
}
}
Throwing an exception on its own isn't very useful, but when combined with a helpful error message or a debugging
tool, you can detect the problematic assertion, you may also check whether an exception is an assertion exception
by using the following snippet:
try {
// ...
}
catch (e) {
if (e instanceof AssertException) {
// ...
}
}
This function can be used in a way similar to C or Java:
assert(obj != null, 'Object is null');
If obj happens to be null, the following message will be printed in the JavaScript console in Firefox:
uncaught exception: AssertException: Object is null
6. Static Local Variables
Some languages like C++ support the concept of static variables, they are local variables that retain their values
between function calls, JavaScript doesn't have a static keyword or direct support to this technique, however, the
fact that functions are also objects makes simulating this feature possible, the idea is storing the static variable as a
property of the function, suppose that we want to create a counter function, here is a code snippet that shows this
technique in action:
function count() {
if (typeof count.i == 'undefined') {
count.i = 0;
}
return count.i++;
}
When count is called for the first time, count.i is undefined, so the if condition is true and count.i is set to 0, because
we are storing the variable as a property, it's going to retain its value between function calls, thus it can be
considered a static variable.
We can introduce a slight performance improvement to the above function, by removing that if check and initialize
count.i after defining the function:
function count() {
return count.i++;
}
count.i = 0;
While the first example encapsulates all of count's logic in its body, the second example is more efficient, the choice
is up to you.
7. null, undefined, and delete
JavaScript is difference from other programming languages by having both undefined and null values, which may
cause confusion for newcomers. null is a special value that means "no value", null is usually thought of as a special
object because typeof null returns 'object'.
On the other hand, undefined means that the variable has not been declared, or has been declared but not given a
value yet, both of the following snippets display 'undefined':
// i is not declared anywhere in code
alert(typeof i);
var i;
alert(typeof i);
Although that null and undefined are two different types, the == (equality) operator considers them equal, but the
=== (identity) operator doesn't.
JavaScript also has a delete operator that "undefines" an object a property (thanks zproxy), it can be handy in
certain situations, you can apply it to object properties and array members, variables declared with var cannot be
deleted, but implicitly declared variables can be:
var obj = {
val: 'Some string'
}
alert(obj.val); // displays 'Some string'
delete obj.val;
alert(obj.val); // displays 'undefined'
8. Deep Nesting of Objects
If you need to do multiple operations on a deeply nested object, it's better to store a reference to it in a temporary
variable instead of dereferencing it each time, for example, suppose that you want to do a series of operations on a
textfield accessible by the following construct:
document.forms[0].elements[0]
It's recommended that you store a reference to the textfield in a variable, and use this variable instead of the above
construct:
var field = document.forms[0].elements[0];
// Use field in loop
Each dot results in an operation to retrieve a property, in a loop, these operations do add up, so it's better to do it
once, store the object in a variable, and re-use it.
9. Using FireBug
Firefox has a fabulous extension for debugging JavaScript code called FireBug, it offers an object inspector, a
debugger with breakpoints and stack views, and a JavaScript console, it can also monitor Ajax requests. In
addition, the extension provides a set of JavaScript functions and objects to simplify debugging, you may explore
them in detail at FireBug's documentation page, here are some that I find most useful:
$ and $$
Those familiar with Prototype will immediately recognize these two functions, $() takes a string parameter and
returns the DOM element whose id is the passed string.
$('nav') // returns the element whose id is #nav.
$$() returns an array of DOM elements that satisfy the passed CSS selector.
$$('div li.menu') // returns an array of li elements that are
// located inside a div and has the .menu class
console.log(format, obj1, ...)
The console object provides methods for displaying log messages in the console, it's more flexible than calling alert,
the console.log() method is similar to C's printf, it takes a formatting string and optional additional parameters, and
outputs the formatted string to the console:
var i = 1;
console.log('i value is %d', i);
// prints:
// i value is 3
console.trace()
This method prints a stack trace where it's called, it doesn't have any parameters.
inspect(obj)
This function takes one parameter, it switches to the inspection tab and inspects the passed object.
—
JavaScripts Guides: Beginner, Advanced
JavaScripts Tutorials: Beginner, Advanced
[Home] [Templates] [Blog] [Forum] [Directory] JavaScript Guides Advanced -
9 JavaScript Tips You May Not Know
|
